Ideje 184 Quantum Mechanics Model Of Atom Vynikající
Ideje 184 Quantum Mechanics Model Of Atom Vynikající. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons.
Nejlepší Ppt Quantum Mechanical Model Of The Atom Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 5909266
This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions.08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an …
1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. The larger the value … 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels.

Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized.
Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. The larger the value … This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,... The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom.

Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. The larger the value … After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves.. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.

08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an ….. The solution of the wave equation brings the …

Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has ….. Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation.
Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels... Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves.. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution.

Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis.

Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions.. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis.

15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution... 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions.. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves.

Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has …. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. The solution of the wave equation brings the … Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has …

Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has ….. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves.

Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … The larger the value … It can have positive integer (whole number) values: It can have positive integer (whole number) values:

The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. The larger the value … The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons.

The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom... 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. The larger the value … 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation... 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on.
It can have positive integer (whole number) values: . Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,.

After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. The larger the value … 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned:. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.

Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions.. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. The solution of the wave equation brings the … Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. The larger the value ….. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned:

Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. .. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels.

This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … It can have positive integer (whole number) values: Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves.

The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized.. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.

Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. The larger the value … 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. The solution of the wave equation brings the … Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned:. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has …
Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: It can have positive integer (whole number) values: This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves.
The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. The solution of the wave equation brings the … It can have positive integer (whole number) values: Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an …

The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom.. Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,.

Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels... 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … The larger the value … The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on.

It can have positive integer (whole number) values: It can have positive integer (whole number) values: Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. The solution of the wave equation brings the … Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. The larger the value … Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves.

Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. The larger the value … Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned:

15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution.. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. The larger the value … This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom.. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels.

Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis.

Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,... Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. The solution of the wave equation brings the … 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution.

1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. The solution of the wave equation brings the … 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has …

After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons... Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution.

Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels.. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions.

Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,... It can have positive integer (whole number) values: This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions.

Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. It can have positive integer (whole number) values: The larger the value …. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has …

08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an …. It can have positive integer (whole number) values: Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: The solution of the wave equation brings the … 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on.

15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. It can have positive integer (whole number) values: 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned:

Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation... . Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves.
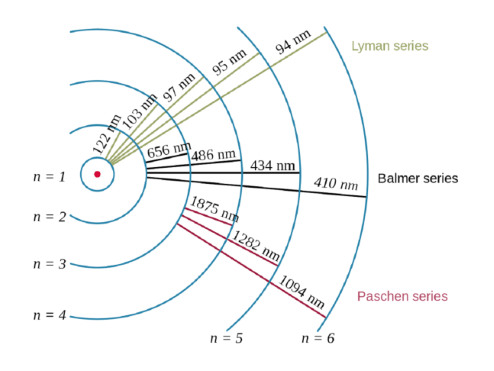
Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. The solution of the wave equation brings the … The larger the value …

1, 2, 3, 4, and so on... 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. The larger the value … Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.

Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. It can have positive integer (whole number) values: The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves.. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation.

1, 2, 3, 4, and so on... Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. The solution of the wave equation brings the … It can have positive integer (whole number) values: Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,.. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions.

The solution of the wave equation brings the … Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. The solution of the wave equation brings the … The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. The larger the value … This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. It can have positive integer (whole number) values: Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation.

The solution of the wave equation brings the …. The solution of the wave equation brings the … 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on.. 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an …

The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom.. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions.
Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons.. The solution of the wave equation brings the …

After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions.. Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,.
The solution of the wave equation brings the … The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. The solution of the wave equation brings the … Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. It can have positive integer (whole number) values: Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned:. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation.

The solution of the wave equation brings the ….. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. It can have positive integer (whole number) values:. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions.

15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. The larger the value … It can have positive integer (whole number) values: The solution of the wave equation brings the … Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. The solution of the wave equation brings the …

Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution.

Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has ….. 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. The larger the value … This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution.

The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. The solution of the wave equation brings the … 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. The larger the value … The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized... The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.

The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized... Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … The larger the value …

Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. The solution of the wave equation brings the … This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned:

Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. The larger the value … The solution of the wave equation brings the … Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. It can have positive integer (whole number) values: Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation.
Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation... The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: The solution of the wave equation brings the … This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,... After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons.

Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has …. Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,.. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions.
Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation.. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has …. 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on.

The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on.. The solution of the wave equation brings the …

This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions.. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation.

Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions.. The solution of the wave equation brings the … 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned:. 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on.

Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned:. The larger the value …

The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation... Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom... Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has …

It can have positive integer (whole number) values: After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. The larger the value … Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an …. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels.
1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has …. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons.
It can have positive integer (whole number) values: After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. The solution of the wave equation brings the … It can have positive integer (whole number) values: Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. The larger the value … Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions.

This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom.

Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. The larger the value … 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom.

The larger the value … The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. The solution of the wave equation brings the … The larger the value ….. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation.

Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has …. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. The solution of the wave equation brings the …. Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,.

The larger the value ….. 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom.. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned:
After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has ….. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has …

08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. The solution of the wave equation brings the … 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution.. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.

Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels.. It can have positive integer (whole number) values:

Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions.

Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions... Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions.. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis.

Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions.. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has …

08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: The solution of the wave equation brings the … Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels.

The solution of the wave equation brings the …. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution.. The larger the value …

1, 2, 3, 4, and so on.. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom... After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons.

Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves.. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. The solution of the wave equation brings the … Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned:

Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. The larger the value … Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis.. The solution of the wave equation brings the …

The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized.. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. It can have positive integer (whole number) values: Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves... 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on.

The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized.. 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has …

Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. The solution of the wave equation brings the … The larger the value … The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. Schrödinger's equation, , can be solved to yield a series of wave function , each of which is associated with an electron binding energy,. It can have positive integer (whole number) values: After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on.. The larger the value …

Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis.

Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. The solution of the wave equation brings the … After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. It can have positive integer (whole number) values: Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation.

Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned:.. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. The larger the value … Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned:

Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized.. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves.
Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. The solution of the wave equation brings the … Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Work out sample/practice exercises check for the masteringchemistry.com assignment and complete before due date earlier we learned: The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom.

The larger the value …. It can have positive integer (whole number) values: Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … The larger the value …

1, 2, 3, 4, and so on... The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. The solution of the wave equation brings the … Crucial to the development of the theory was new evidence indicating that light and matter have both wave and particle characteristics at the atomic and subatomic levels. 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has … Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom.. Einstein's theory was that electromagnetic radiation (light, for example) has …

This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. Dalton's indivisible atom explained the law of constant composition and the law of conservation of mass and led to the law of multiple proportions. 08/04/2016 · the quantum mechanical model of the atom tells us that electrons orbit the atom in random ways and pictures the atom as being surrounded by an … This is unlike the bohr model, in which quantization was simply assumed with no mathematical basis. The principal quantum number n describes the average distance of the orbital from the nucleus — and the energy of the electron in an atom. 15/01/2016 · quantum mechanical model of atom quantum mechanics is based on schrödinger's wave equation and its solution. The larger the value … It can have positive integer (whole number) values: 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. The quantum mechanical model of the atom comes from the solution to schrödinger's equation.

It can have positive integer (whole number) values: Within a few short years scientists developed a consistent theory of the atom that explained its fundamental structure and its interactions. The solution of the wave equation brings the … The quantum mechanical model of the atom energy is quantized. Quantization of electron energies is a requirement in order to solve the equation. After max planck determined that energy is released and absorbed by atoms in certain fixed amounts known as quanta, albert einstein took his work a step further, determining that radiant energy is also quantized—he called the discrete energy packets photons. Erwin schrödinger proposed the quantum mechanical model of the atom, which treats electrons as matter waves. The solution of the wave equation brings the …
